The Vital Role of Gonadotropins in Assisted Reproductive Technology
March 19, 2025, 5:24 p.m.
Gonadotropins are powerful hormones that play a big part in assisted reproductive technology (ART). These fertility drugs stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs, raising the odds of pregnancy in treatments like in vitro fertilization (IVF). This article explores their role, how they work, and why they matter.

So, what exactly are gonadotropins? They’re hormones made by the pituitary gland in your brain. In women, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) control the menstrual cycle and trigger ovulation. In men, they help produce sperm. In ART, doctors use synthetic gonadotropins to mimic these natural effects.
In assisted reproductive technology, the goal is to get multiple eggs at once. Why? Because more eggs mean better chances of fertilization and a healthy embryo. For couples facing infertility, gonadotropins are a game-changer, making treatments like IVF more effective.
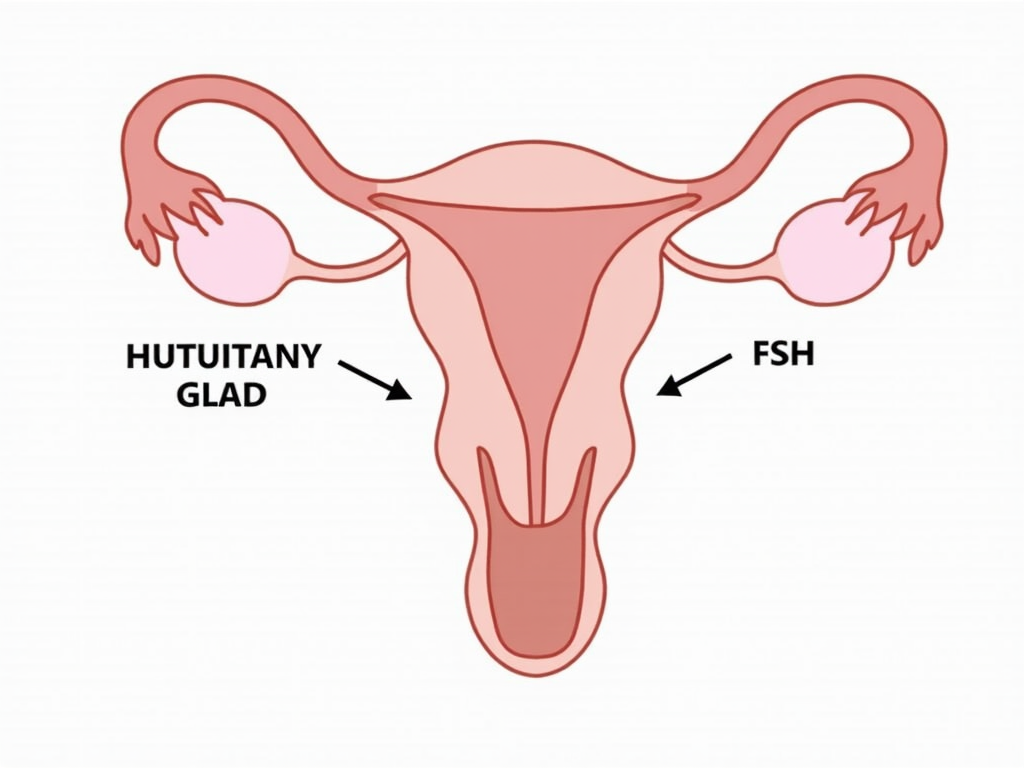
I’ve worked with many patients as a fertility specialist, and the role of gonadotropins in assisted reproductive technology always stands out. By fine-tuning the dose, we can help a woman’s ovaries produce just the right number of eggs. It’s amazing to see hope turn into results.
There are a few types of gonadotropins used in ART. Recombinant FSH is made in a lab and is super pure. Human menopausal gonadotropin (hMG) comes from the urine of postmenopausal women and has both FSH and LH. Then there’s human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) to trigger egg release.
Here’s a quick look at these fertility drugs in action:
| Type | Source | Job | Possible Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recombinant FSH | Lab-made | Grows egg follicles | Bloating, multiple births |
| hMG | Urine extraction | Boosts FSH and LH | Swelling, discomfort |
| hCG | Lab or urine | Releases eggs | Allergic reactions, swelling |
How do you take gonadotropins? They come as injections, usually given daily. Patients learn to give themselves these shots at home. It might sound scary, but with a nurse’s help, it becomes routine. The key is sticking to the schedule for the best results.

Monitoring is everything when using gonadotropins. Doctors use ultrasounds to watch the ovaries and blood tests to check hormone levels. This helps them adjust the dose to avoid problems like ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS), where the ovaries overreact and swell up.
Side effects can happen, though they’re usually mild. Some people feel bloated or moody. More serious risks, like OHSS or twins, are rare but manageable with care. Open talks with your doctor can keep things on track.
How well do gonadotropins work? Studies show IVF success rates hover around 30-40% per cycle with these drugs. That number depends on age, health, and infertility causes, but it’s clear gonadotropins make a big difference.
One patient told me, ‘The shots were tough at first, but I kept picturing my future family. When the test came back positive, every pinch was worth it.’ Stories like hers show why gonadotropins matter in fighting infertility.

Here are some tips if you’re starting gonadotropin therapy:
- Get the Technique Down: Practice with your nurse until you’re confident.
- Stay on Time: Set reminders for your shots.
- Watch Your Body: Tell your doctor about pain or odd symptoms right away.
- Take Care of Yourself: Eat well and rest to feel your best.
The role of gonadotropins in assisted reproductive technology can’t be overstated. They help produce more eggs, boost success rates, and bring hope to those struggling with infertility. With careful use, these fertility drugs turn dreams into reality for so many.
