Understanding How Gonadotropins Affect Ovulation: A Comprehensive Guide
March 29, 2025, 5:35 p.m.
Introduction
Gonadotropins are hormones that play a crucial role in regulating ovulation, the process where a mature egg is released from the ovary. These hormones, produced by the pituitary gland, are vital for reproductive health and are often used in fertility treatments to help women conceive. In this article, we will explore how gonadotropins affect ovulation, their role in the menstrual cycle, and their use in treating infertility.
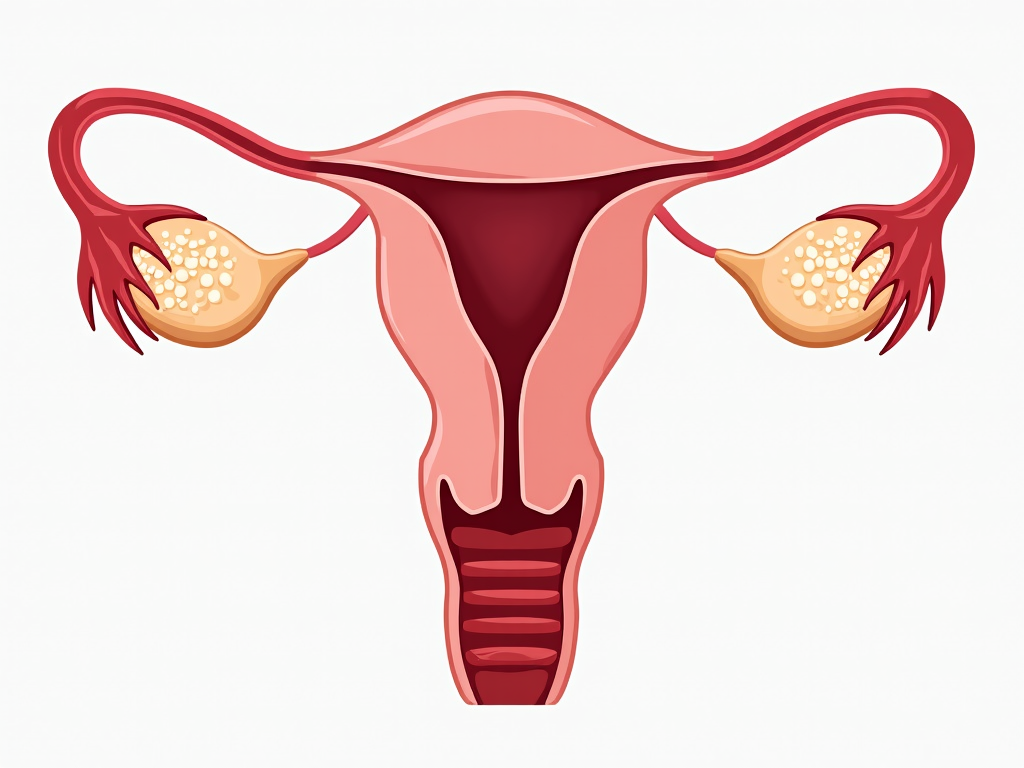
What Are Gonadotropins?
Gonadotropins are a group of hormones that stimulate the gonads (ovaries in women and testes in men). The two primary gonadotropins involved in ovulation are:
- Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH): Responsible for the growth and maturation of ovarian follicles, which contain the eggs.
- Luteinizing Hormone (LH): Triggers the release of the mature egg from the follicle during ovulation.
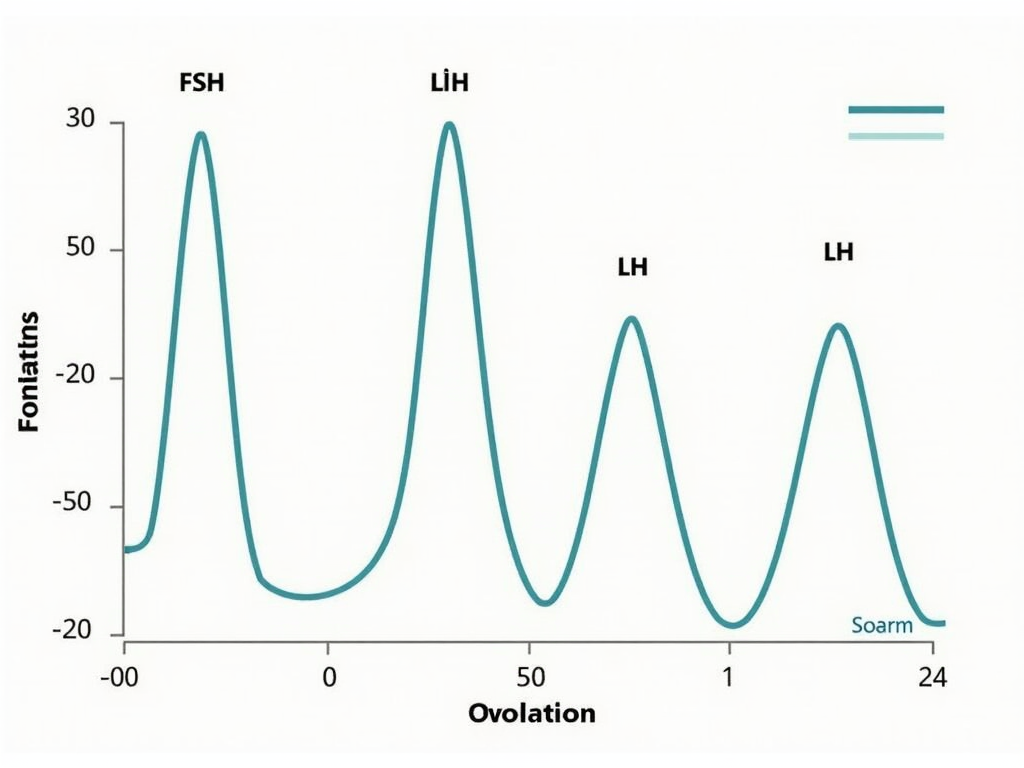
These hormones are produced by the pituitary gland and are regulated by the hypothalamus through gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). Together, FSH and LH ensure the proper functioning of the menstrual cycle and ovulation.
The Menstrual Cycle and Ovulation
The menstrual cycle is a monthly process that prepares the body for pregnancy. It consists of several phases, each regulated by hormones, including gonadotropins:
- Menstrual Phase: The cycle begins with menstruation, where the uterine lining is shed.
- Follicular Phase: FSH stimulates the growth of ovarian follicles. As follicles mature, they produce estrogen, which thickens the uterine lining.
- Ovulation: A surge in LH triggers the release of the mature egg from the dominant follicle.
- Luteal Phase: After ovulation, the ruptured follicle forms the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone to prepare the uterus for a potential pregnancy.
Gonadotropins are essential for these processes, ensuring that the follicles develop properly and that ovulation occurs at the right time.
Gonadotropins in Fertility Treatments
For women struggling with infertility, gonadotropins are often used as fertility drugs to stimulate ovulation. These treatments are common in assisted reproductive technologies (ART) such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) and intrauterine insemination (IUI).
Types of Gonadotropin Medications
- Human Menopausal Gonadotropin (hMG): Contains both FSH and LH.
- Recombinant FSH: A synthetic form of FSH.
- Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG): Mimics LH to trigger ovulation.
How Gonadotropins Are Administered
Gonadotropin treatments typically involve daily injections. The dosage and timing are carefully monitored to avoid overstimulating the ovaries, which can lead to complications like ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS).
Monitoring During Treatment
During treatment, women undergo regular ultrasounds and blood tests to track follicle development and hormone levels. This ensures the treatment is working effectively and safely.

Personal Insights and Experiences
Undergoing fertility treatments with gonadotropins can be an emotional and physical journey. Many women experience a mix of hope, anxiety, and frustration as they navigate the process. It's common to feel overwhelmed by the injections, appointments, and waiting periods.
However, remember that you're not alone. Building a support system—whether it's your partner, family, or a support group—can make a significant difference. Keeping a journal to track your emotions and physical symptoms can also help you communicate better with your healthcare provider and manage the ups and downs of treatment.

Potential Side Effects and Risks
While gonadotropins are effective, they come with potential side effects and risks:
- Common Side Effects:
- Bloating
- Headaches
- Mood swings
-
Injection site reactions
-
Serious Risks:
- Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS): A condition where the ovaries become swollen and painful due to overstimulation.
- Multiple Pregnancies: Increased chance of twins or triplets, which can pose health risks for both mother and babies.
It's crucial to work closely with your healthcare provider to minimize these risks and ensure the treatment is tailored to your needs.
Conclusion
Gonadotropins are vital hormones that regulate ovulation and are a cornerstone of fertility treatments for women facing infertility. By understanding how they work, you can make informed decisions about your reproductive health. If you're considering fertility treatments, consult with your healthcare provider to determine the best approach for your situation. Remember, every journey is unique, and support is available to help you along the way.